SELECT * FROM branch;
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
column3 datatype,
....
);
Typy danych w kolumnach
Text data types:
SQL Wildcards = Regular Expressions
-- % = any # characters, _ = one character
-- fin any client who are in LCC
SELECT *
FROM client
WHERE client_name LIKE '%LLC';
SELECT *
FROM branch_supplier
WHERE supplier_name LIKE '% Label%';
-- find any employee born in October
SELECT *
FROM employee
WHERE birth_day LIKE '____-02%';
-- find any client who are schools
SELECT *
FROM client
WHERE client_name LIKE '%school%';
UNION - selection from multiply tables
-- find a list of employee and branch names
-- Union works only for the same number of columns X UNION X
SELECT first_name AS Company_Names
FROM employee
UNION
SELECT branch_name
FROM branch
UNION
SELECT client_name
FROM client;
NESTED QUERIES - more SELECT statements
SELECT employee.first_name, employee.last_name
FROM employee
WHERE employee.emp_id IN (
SELECT works_with.emp_id FROM works_with
WHERE works_with.total_sales > 30000
);
VARCHAR (40) - string z ograniczoną liczbą znaków
TEXT - string
BLOB - Binary Larg Objects - 65000 bytes of data
ENUM('X','Y','Z') - list of values in order we enter them
SET - values are ENUM up to 64 list items
SQL Keywords:
Number data types:
INT (size) - integer
FLOAT(size,d) - small number with floating decimal point, d - decimal point
DOUBLE(size,d) large number with floating decimal point
Date data types:
DATE() - YYYY-MM-DD
TIMESTAMP()
TIME()
SQL Keywords:
ADD - add column
ALTER - add delete modify columns in table or change data types of column in table
CREATE - create database, table, index, view, procedure
- CREATE DATABASE
- CREATE TABLE
- CREATE INDEX
- CREATE VIES
DELETE - delete rows from table
DESC - sort results descending order
DROP - delete column, constrains, database, index table or view
- DROP COLUMN
- DROP DATABASE
- DROP INDEX
- DROP CONSTRAINS
- DROP TABLE
FOREIGN KEY - a constrain that is key used to link two tables together
UPDATE - updates existing rows in table
SELECT DISTINCT - find out all different values from specific column and table
SELECT DISTINCT - find out all different values from specific column and table
https://www.w3schools.com/sql/sql_ref_keywords.asp
FUNKCIONS:
block of code which can calculate some values - count, average
COUNT(column name)
-- find the number of employees
SELECT COUNT(super_id)
FROM employee;
-- find female employees born after 1970
SELECT COUNT(emp_id)
FROM employee
WHERE sex = 'F' AND birth_day > '1971-01-01'
-- find the average of all employee's salaries
SELECT AVG(salary)
FROM employee
WHERE sex = 'M';
-- find the sum of all salaries
SELECT SUM(salary)
FROM employee;
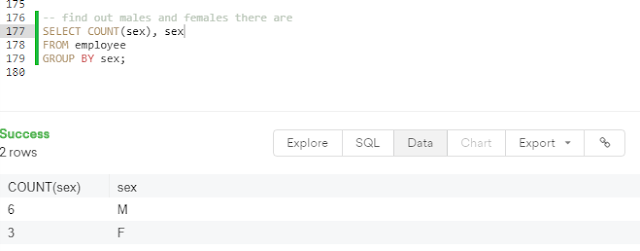
Aggregation:
SELECT COUNT(column_name), column_name
FROM table_name
GROUP BY value;
FUNKCIONS:
block of code which can calculate some values - count, average
COUNT(column name)
-- find the number of employees
SELECT COUNT(super_id)
FROM employee;
-- find female employees born after 1970
SELECT COUNT(emp_id)
FROM employee
WHERE sex = 'F' AND birth_day > '1971-01-01'
-- find the average of all employee's salaries
SELECT AVG(salary)
FROM employee
WHERE sex = 'M';
-- find the sum of all salaries
SELECT SUM(salary)
FROM employee;
Aggregation:
SELECT COUNT(column_name), column_name
FROM table_name
GROUP BY value;
SQL Wildcards = Regular Expressions
-- % = any # characters, _ = one character
-- fin any client who are in LCC
SELECT *
FROM client
WHERE client_name LIKE '%LLC';
SELECT *
FROM branch_supplier
WHERE supplier_name LIKE '% Label%';
-- find any employee born in October
SELECT *
FROM employee
WHERE birth_day LIKE '____-02%';
-- find any client who are schools
SELECT *
FROM client
WHERE client_name LIKE '%school%';
UNION - selection from multiply tables
-- find a list of employee and branch names
-- Union works only for the same number of columns X UNION X
SELECT first_name AS Company_Names
FROM employee
UNION
SELECT branch_name
FROM branch
UNION
SELECT client_name
FROM client;
-- find a list of all clients and branch suppliers names
SELECT client_name, client.branch_id
FROM client
UNION
SELECT supplier_name, branch_supplier.branch_id
FROM branch_supplier;
JOIN - join columns from different tables
JOIN - join columns from different tables
Here are the different types of the JOINs in SQL:
- (INNER) JOIN: Returns records that have matching values in both tables
- LEFT (OUTER) JOIN: Return all records from the left table, and the matched records from the right table
- RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: Return all records from the right table, and the matched records from the left table
- FULL (OUTER) JOIN: Return all records when there is a match in either left or right table
NESTED QUERIES - more SELECT statements
SELECT employee.first_name, employee.last_name
FROM employee
WHERE employee.emp_id IN (
SELECT works_with.emp_id FROM works_with
WHERE works_with.total_sales > 30000
);
ON DELETE CASCADE
ON DELETE SET

Komentarze
Prześlij komentarz